- HOME
- CONSULTATIONS
- MAIN PROCEDURES
- TOPICS
- Celiac Disease
- Constipation
- Lactose Intolerance
- Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome
- H Pylori and Peptic Ulcers
- Digestive System: How it Works
- Heartburn
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Polyps
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Crohn's Disease
- Gallstones
- Pancreatitis
- Hemorrhoids
- Diverticular Disease
- Abdominal Adhesions
- FODMAPs
- Non Celiac Gluten Sensitivity
- RESEARCH
- BIOGRAPHY
- LINKS
TOPICS
Hemorrhoids
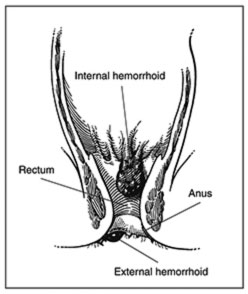
Hemorrhoids are swollen and inflamed veins around the anus or in the lower rectum. The rectum is the last part of the large intestine leading to the anus. The anus is the opening at the end of the digestive tract where bowel contents leave the body.
External hemorrhoids are located under the skin around the anus. Internal hemorrhoids develop in the lower rectum. Internal hemorrhoids may protrude, or prolapse, through the anus. Most prolapsed hemorrhoids shrink back inside the rectum on their own. Severely prolapsed hemorrhoids may protrude permanently and require treatment.
-
What are the symptoms of Hemorrhoids?
The most common symptom of internal hemorrhoids is bright red blood on stool, on toilet paper, or in the toilet bowl after a bowel movement. Internal hemorrhoids that are not prolapsed are usually not painful. Prolapsed hemorrhoids often cause pain, discomfort, and anal itching.
Blood clots may form in external hemorrhoids. A blood clot in a vein is called a thrombosis. Thrombosed external hemorrhoids cause bleeding, painful swelling, or a hard lump around the anus. When the blood clot dissolves, extra skin is left behind. This skin can become irritated or itch.
Excessive straining, rubbing, or cleaning around the anus may make symptoms, such as itching and irritation, worse.
Hemorrhoids are not dangerous or life threatening. Symptoms usually go away within a few days, and some people with hemorrhoids never have symptoms. -
How common are Hemorrhoids?
About 75 percent of people will have hemorrhoids at some point in their lives. Hemorrhoids are most common among adults ages 45 to 65. Hemorrhoids are also common in pregnant women.
-
What causes hemorrhoids?
Swelling in the anal or rectal veins causes hemorrhoids. Several factors may cause this swelling, including
- chronic constipation or diarrhea
- straining during bowel movements
- sitting on the toilet for long periods of time
- a lack of fiber in the diet
Another cause of hemorrhoids is the weakening of the connective tissue in the rectum and anus that occurs with age.
Pregnancy can cause hemorrhoids by increasing pressure in the abdomen, which may enlarge the veins in the lower rectum and anus. For most women, hemorrhoids caused by pregnancy disappear after childbirth. -
How are hemorrhoids diagnosed?
The doctor will examine the anus and rectum to determine whether a person has hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoid symptoms are similar to the symptoms of other anorectal problems, such as fissures, abscesses, warts, and polyps.
The doctor will perform a physical exam to look for visible hemorrhoids. A digital rectal exam with a gloved, lubricated finger and an anoscope, a hollow, lighted tube, may be performed to view the rectum.
A thorough evaluation and proper diagnosis by a doctor is important any time a person notices bleeding from the rectum or blood in the stool. Bleeding may be a symptom of other digestive diseases, including colorectal cancer.
Additional exams may be done to rule out other causes of bleeding, especially in people age 40 or older:
- Colonoscopy. A flexible, lighted tube called a colonoscope is inserted through the anus, the rectum, and the upper part of the large intestine, called the colon. The colonoscope transmits images of the inside of the rectum and the entire colon.
- Sigmoidoscopy. This procedure is similar to colonoscopy, but it uses a shorter tube called a sigmoidoscope and transmits images of the rectum and the sigmoid colon, the lower portion of the colon that empties into the rectum.
- Barium enema x ray. A contrast material called barium is inserted into the colon to make the colon more visible in x ray pictures.
-
How are hemorrhoids treated?
At-home Treatments
Simple diet and lifestyle changes often reduce the swelling of hemorrhoids and relieve hemorrhoid symptoms. Eating a high-fiber diet can make stools softer and easier to pass, reducing the pressure on hemorrhoids caused by straining.
Fiber is a substance found in plants. The human body cannot digest fiber, but fiber helps improve digestion and prevent constipation. Good sources of dietary fiber are fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. On average, Americans eat about 15 grams of fiber each day. The American Dietetic Association recommends 25 grams of fiber per day for women and 38 grams of fiber per day for men.
Doctors may also suggest taking a bulk stool softener or a fiber supplement such as psyllium or methylcellulose.
Other changes that may help relieve hemorrhoid symptoms include
- drinking six to eight 8-ounce glasses of water or other nonalcoholic fluids each day
- sitting in a tub of warm water for 10 minutes several times a day
- exercising to prevent constipation
- not straining during bowel movements
Over-the-counter creams and suppositories may temporarily relieve the pain and itching of hemorrhoids. These treatments should only be used for a short time because long-term use can damage the skin.
Medical Treatment
If at-home treatments do not relieve symptoms, medical treatments may be needed. Outpatient treatments can be performed in a doctor's office or a hospital. Outpatient treatments for internal hemorrhoids include the following:
- Rubber band ligation. The doctor places a special rubber band around the base of the hemorrhoid. The band cuts off circulation, causing the hemorrhoid to shrink. This procedure should be performed only by a doctor.
- Sclerotherapy. The doctor injects a chemical solution into the blood vessel to shrink the hemorrhoid.
- Infrared coagulation. The doctor uses heat to shrink the hemorrhoid tissue.
Large external hemorrhoids or internal hemorrhoids that do not respond to other treatments can be surgically removed.
Points to remember:
- Hemorrhoids are swollen and inflamed veins around the anus or in the lower rectum.
- Hemorrhoids are not dangerous or life threatening, and symptoms usually go away within a few days.
- A thorough evaluation and proper diagnosis by a doctor is important any time a person notices bleeding from the rectum or blood in the stool.
- Simple diet and lifestyle changes often reduce the swelling of hemorrhoids and relieve hemorrhoid symptoms.
- If at-home treatments do not relieve symptoms, medical treatments may be needed.
OTHER TOPICS
Celiac Disease
Constipation
Lactose Intolerance
Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome (CVS)
H Pylori and Peptic Ulcers
Digestive System: How it Works
Heartburn
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Polyps
Ulcerative Colitis
Crohn's Disease
Gallstones
Pancreatitis
Hemorrhoids
Diverticular Disease
Abdominal Adhesions
FODMAPs
Non Celiac Gluten Sensitivity

